When travelers plan their trips, landmark recommendation systems considering the properties of their trip will be convenient to help travelers determine locations they will visit.
We propose an approach to extracting and recommending landmark locations related to a user’s trip from social images. We first examine the impact of spatial and temporal properties of a trip on the distribution of popular places through large-scale data analysis. Second, we present an approach that efficiently extracts landmarks from social media and recommends user-centered landmarks. Our approach is to construct a vector that weights frequently visited places under the similar conditions of a traveler, and then to re-rank landmarks based on the vector. We provide users with the user-centered recommended landmarks, together with regions visited by travelers who visited the recommended landmarks together.

According to our experimental results, the approach enhanced the accuracy of recommended landmarks by 41% in the size of a city and by 65% in the size of a state, compared to a baseline. Through a user study, we also verified that it is applicable to lesser-known places where the social media images are small in quantity. Thus, we expect that the approach is helpful in developing personalized recommendations.
In recent years, social media websites, such as Twitter, Facebook have gained in popularity and have become ubiquitous in our daily lives, where rich user-generated texts are propagated through social networks. Topic models, such as Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), have been proposed and shown to be useful for text analysis. The existing topic models focus on traditional document collections, which consist of a relatively small number of long and high-quality documents. However, user-generated texts tend to be shorter and noisier than traditional content.
Besides, the social networks have two novel features: context information on nodes, such as user features, and edges, such as relationship, which have not been considered by the existing topic models. In this work, we pose the problem of finding user topics in large-scale collection of documents from online social networks for recommending socially personalized content reflecting social relationship between social networking service (SNS) users.
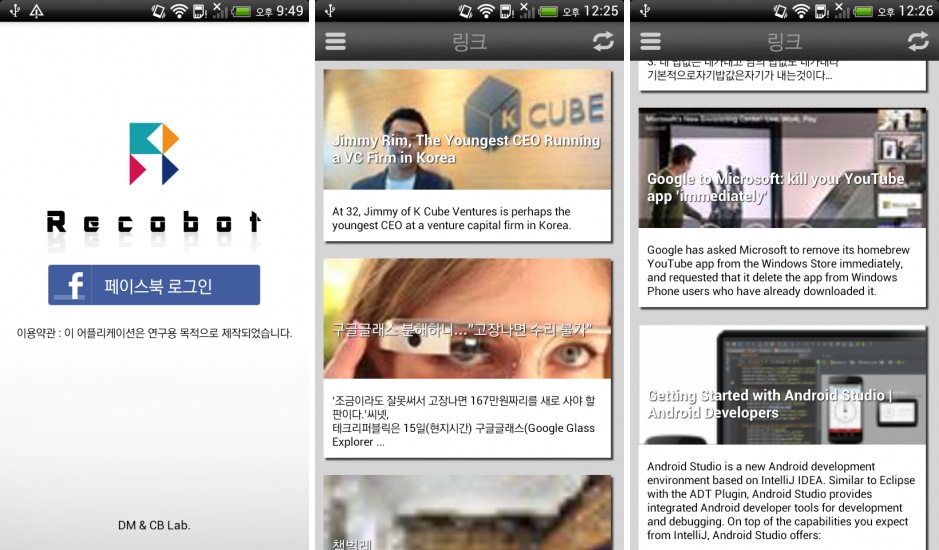
Nowadays, huge amount of data generated on social media. Also traffic from mobile device surpass the traffic from web. Therefore, recommendation system becomes important more and more. We will provide recommendation framework for users who use mobile device. To do this, we started to implement link recommendation framework for Android user using Facebook data.